12 January 2015
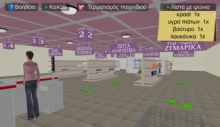
Thessaloniki, Greece – Greek researchers demonstrated the potential of a virtual supermarket cognitive training game as a screening tool for patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among a sample of older adults. MCI is a condition that often predates Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and is characterized by memory loss and inability to execute complex activities such as financial planning.
So far virtual reality game–based applications and especially virtual supermarkets have been used as cognitive training applications and as measures of cognitive functions, although it has been shown that they can detect MCI only when used in combination with standardized neuropsychological tests. However scientists from the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (AUTH), the Greek Association of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders (GAADRD) and the Centre for Research and Technology Hellas/Information Technologies Institute (CERTH/ITI) have succeeded in making the shift to MCI screening via robust virtual reality game applications that can be used on their own for accurate MCI detection. In an article published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, the researchers have indicated that the virtual supermarket (VSM) application displayed a correct classification rate (CCR) of 87.30%, achieving a level of diagnostic accuracy similar to standardized neuropsychological tests, which are the gold standard for MCI screening. Patients with MCI can live independently and not all such patients progress to AD. Therefore the global effort against cognitive disorders is focused on early detection at the MCI stage.

Caption: The VSM virtual environment
A large number of older adults use computerized cognitive training exercises/games as an easy and enjoyable means of exercising their brain. If these games and exercises can also detect cognitive disorders, the whole cognitive screening process could become more pleasurable, thus motivating more people to be evaluated. With the majority of older adults examining their cognitive health regularly through such games, possible cognitive impairment will be detected at the MCI stage thus allowing patients to enjoy a better quality of life and remain independent for a longer time.
The use of the VSM as a robust screening test could have profound implications for the diagnosis and treatment of MCI, the most important of which is the possibility for automated remote MCI screening. The performance of older adults playing such a game at home could be monitored and an algorithm embedded in the game could inform them when their performance suggests possible cognitive impairment due to MCI, prompting them to visit an appropriate health service. Such a system would have the ability to screen the majority of older adults effectively, while at the same time minimizing examination costs. As computer applications increasingly become embedded in our work and social life, they could also become part of our preventive healthcare. Research on the use of the VSM for remote assessment is already underway and the results of that study will be published soon.
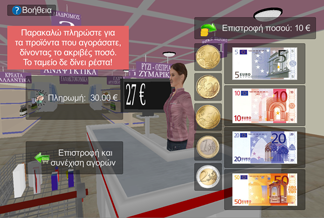
Caption: The VSM payment screen
The VSM has been developed as part of the “Εν-ΝΟΗΣΗΣ” project for the use of new technologies in the screening, diagnosis, treatment and support of patients with MCI. Its development, testing and research application have been undertaken by research organizations that have been heavily involved in the transfer and dissemination of high-quality research knowledge, advanced solution development and leading-edge technologies. The same organizations are currently involved in the development and trialing of other novel technological instruments that respond to a number of clinical and organizational needs in the effort against cognitive disorders.
# # #
NOTES FOR EDITORS
Can a Virtual Reality Cognitive Training Application Fulfill a Dual Role? Using the Virtual Supermarket Cognitive Training Application as a Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment, by Stelios Zygouris, Dimitrios Giakoumis, Konstantinos Votis, Stefanos Doumpoulakis, Konstantinos Ntovas, Sofia Segkouli, Charalampos Karagiannidis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, and Magda Tsolaki, DOI: 10.3233/JAD-141260, Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, published online in advance of Volume 44, Issue 4 by IOS Press.
Contact:
Stelios Zygouris
Research Psychologist
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
+30 2310 268 471
szygouris@gmail.com
About the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (AUTH)
he Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (http://www.auth.gr/) is the largest university in Greece. It comprises 7 faculties that consist of 33 schools, 5 faculties that consist of one school each, as well as 4 independent schools. About 81,500 students study at the Aristotle University (72,140 in undergraduate programs and 8,360 in postgraduate programs). There are 2,150 faculty members: 739 professors, 435 associate professors, 634 assistant professors, and 342 lecturers. There are also 11 teaching assistants, 58 research fellows, 248 members of the Special Laboratory Teaching Personnel (S.L.T.P.), as well as 15 foreign language teachers and 4 foreign instructors. Faculty members are also assisted by 213 members of the Special Technical Laboratory Personnel (S.T.L.P.).
The Aristotle University of Thessaloniki conducts research projects, participates in European research programs, cooperates with international institutions and organizations and attracts outstanding researchers from within Greece and abroad. The Aristotle University supports research projects in a wide variety of disciplines related to the environment (natural and built), computing, new technologies and nanotechnology, telecommunications, industrial technologies, transport, biotechnology, biomedicine and health, agriculture, forestry and fishery, education and language, history and archaeology, social studies and economics.
About the Greek Association of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders (GAADRD)
The Greek Association of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders (http://www.alzheimer-hellas.gr/) is a non-profit organization that was founded in 1995 by relatives of patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, doctors of all specialties (mainly neurologists and psychiatrists) and other experts (such as psychologists, social workers, physiotherapists, etc.) who deal with the problems caused by this disease and other types of dementia. The Association operates 2 day centers in Thessaloniki and has over 4.000 members. It is a member of Alzheimer Europe and Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI) and has successfully participated in various national and European research projects producing new scientific knowledge and innovative interventions for cognitive disorders.
The aim of the Association is to offer information and advice concerning the care of patients with cognitive disorders and provide services for patients and their families. It also strives to offer help and support to caregivers in order to reduce the social, economic and emotional burden deriving from the long term care of people suffering from dementia. Lastly, the Association attempts to publicize the social needs of the affected population and inform the public on issues related to dementia and cognitive disorders in general.
About the Information Technologies Institute (ITI)
The Information Technologies Institute (http://www.iti.gr/), formerly Informatics and Telematics Institute, was established in 1998 in Thessaloniki as a non-profit research organization under the auspices of the General Secretariat of Research and Technology (GSRT) of the Greek Ministry of Development. Since 2000, ITI has joined the Centre for Research and Technology Hellas (CERTH). The main objective of the Institute is to be a research institution of excellence, identifying promising fields for the future and creating an environment that will allow the transfer of basic, applied and technological research in the growth of the digital economy of the 21st century. CERTH/ITI has developed spheres of excellence and critical mass in research and technology in several strategically important fields in a number of areas: Image and Signal Processing, Computer Vision, Human Computer Interaction, Virtual and Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Security and Surveillance, Biomedicine – Bioinformatics, Robotics, ICT for Environment Monitoring, Geosciences and Remote Sensing, Social Network Analysis, Networks and Communications, Cultural and Educational Technology.
About the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (JAD)
The Journal of Alzheimer's Disease (http://www.j-alz.com) is an international multidisciplinary journal to facilitate progress in understanding the etiology, pathogenesis, epidemiology, genetics, behavior, treatment and psychology of Alzheimer's disease. The journal publishes research reports, reviews, short communications, book reviews, and letters-to-the-editor. Groundbreaking research that has appeared in the journal includes novel therapeutic targets, mechanisms of disease and clinical trial outcomes. The Journal of Alzheimer's Disease has an Impact Factor of 3.612 according to Thomson Reuters' 2013 Journal Citation Reports. It is ranked #22 on the Index Copernicus Top 100 Journal List. The Journal is published by IOS Press (www.iospress.com).







