11 May 2021

Investigators review research that shows spiritual fitness and meditation mitigate the negative effects of stress and reduce the risk of memory loss, cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease
Amsterdam, NL – It is projected that up to 152 million people worldwide will be living with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by 2050. To date there are no drugs that have a substantial positive impact on either the prevention or reversal of cognitive decline. A growing body of evidence finds that targeting lifestyle and vascular risk factors have a beneficial effect on overall cognitive performance. A new review in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, published by IOS Press, examines research that finds spiritual fitness, a new concept in medicine that centers on psychological and spiritual wellbeing, and Kirtan Kriya, a simple 12-minute meditative practice, may reduce multiple risk factors for AD.
“The key point of this review is that making a commitment to a brain longevity lifestyle, including spiritual fitness, is a critically important way for aging Alzheimer’s disease free,” explain authors Dharma Singh Khalsa, MD, Alzheimer’s Research and Prevention Foundation, Tucson, AZ, USA, and Andrew B. Newberg, MD, Department of Integrative Medicine and Nutritional Sciences, Department of Radiology, Marcus Institute of Integrative Health, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, USA. “We hope this article will inspire scientists, clinicians, and patients to embrace this new concept of spiritual fitness and make it a part of every multidomain program for the prevention of cognitive disability.”
Research reveals that religious and spiritual involvement can preserve cognitive function as we age. The authors observe that today, spirituality is often experienced outside the context of an organized religion and may be part of every religion or separate to it. Spiritual fitness is a new dimension in AD prevention, interweaving basic, psychological and spiritual wellbeing. The authors discuss the research on how these factors affect brain function and cognition. For example, psychological wellbeing may reduce inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and disability. Significantly, individuals who have a high score on a “purpose of life” (PIL) measure, a component of psychological wellbeing, were 2.4 times more likely to remain free of AD than individuals with low PIL. In another study, participants who reported higher levels of PIL exhibited better cognitive function, and further, PIL protected those with already existing pathological conditions, thus slowing their decline.
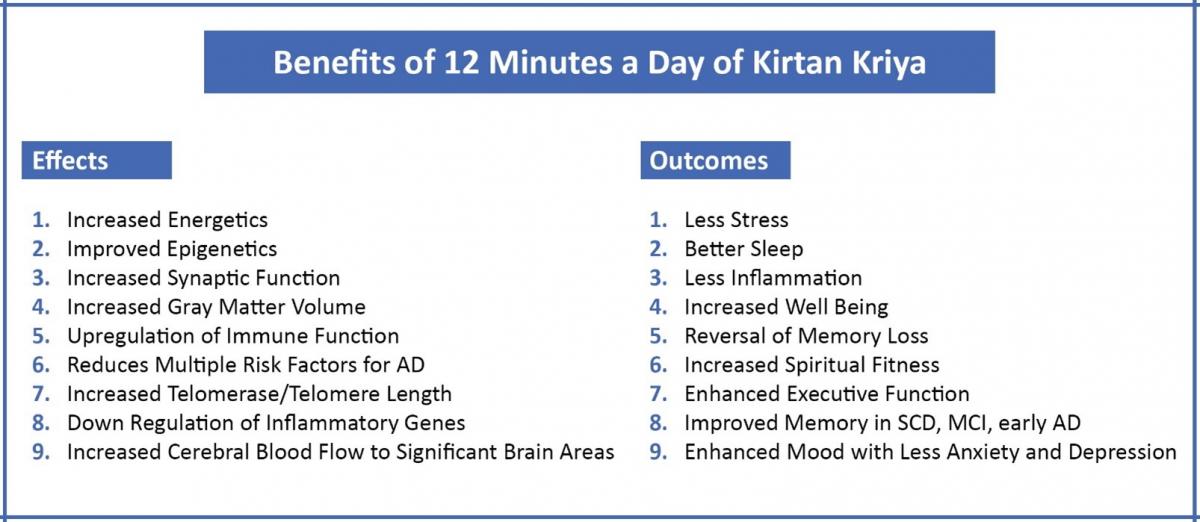
Stress and stress management are under-discussed topics in AD prevention, yet the authors point out that there is ample evidence that physical, psychological, and emotional effects of stress may elevate AD risk. Kirtan Kriya (KK) is a 12-minute singing meditation that involves four sounds, breathing, and repetitive finger movements. It has multiple documented effects on stress, such as improving sleep, decreasing depression, and increasing wellbeing. It has also been found to increase blood flow to areas of the brain involved in cognition and emotional regulation and increases grey matter volume and decreases ventricular size in long-term practitioners, which may slow brain aging. Research in healthy individuals, caregivers, and those with cognitive decline found that the practice improves cognition, slows memory loss, and improves mood.
The overall relationship between spiritual fitness and a person’s complete physical and mental health is a topic of investigation in the emerging field of study called neurotheology. Early work has focused on the development of models regarding which brain areas are affected through spiritual practices such as meditation or prayer. Over the last 20 years, there has been an extensive growth in neuroimaging and other physiological studies evaluating the effect of meditation, spiritual practices, and mystical experiences. A neuroimaging study of KK found long term brain effects, during meditation and afterwards. Neurotheological studies can help understanding of how a practice such as KK can lead to more permanent effects in brain function that support spiritual fitness, according to Dr. Khalsa and Dr. Newberg.
“Mitigating the extensive negative biochemical effects of stress with meditation practices, in tandem with the creation of heightened levels of spiritual fitness, may help lower the risk of AD. Small shifts in one’s daily routine can make all the difference in AD prevention,” Dr. Khalsa and Dr. Newberg conclude. “We are optimistic this article will inspire future research on the topic of spiritual fitness and AD.”
George Perry, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease and Professor of Biology and Chemistry, Semmes Distinguished University Chair in Neurobiology, University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, added, “Living a brain longevity lifestyle including spiritual fitness is the only proven way to prevent this disease.”
###
NOTES FOR EDITORS
Full open access study: “Spiritual Fitness: A New Dimension in Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention” by Dharma Singh Khalsa and Andrew B. Newberg (DOI: 10.3233/JAD-201433), published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, Volume 80, Issue 2 (2021). The article is freely available at: content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-alzheimers-disease/jad201433. The journal is published by IOS Press.
Instructions on practicing Kirtan Kriya are offered in the Supplementary Material.
Contact
To request the full text of the article or further information please contact Diana Murray, IOS Press (+1 718-640-5678 or d.murray@iospress.com). To reach the authors for comment, please contact Dharma Singh Khalsa, MD (drdharma@alzheimersprevention.org) or Andrew B. Newberg, MD (andrew.newberg@jefferson.edu). For questions about the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, please contact George Perry (+1 210-458-8660 or george.perry@utsa.edu).
About the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease
Now in its 24th year of publication, the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease (JAD) is an international multidisciplinary journal to facilitate progress in understanding the etiology, pathogenesis, epidemiology, genetics, behavior, treatment, and psychology of Alzheimer's disease. The journal publishes research reports, reviews, short communications, book reviews, and letters-to-the-editor. Groundbreaking research that has appeared in the journal includes novel therapeutic targets, mechanisms of disease, and clinical trial outcomes. JAD has a Journal Impact Factor of 3.909 according to Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate, 2020). j-alz.com
About IOS Press
IOS Press is headquartered in Amsterdam with satellite offices in the USA, Germany, India, and China and serves the information needs of scientific and medical communities worldwide. IOS Press now publishes more than 90 international peer-reviewed journals and about 70 book titles each year on subjects ranging from computer science, artificial intelligence, and engineering to medicine, neuroscience, and cancer research. iospress.com